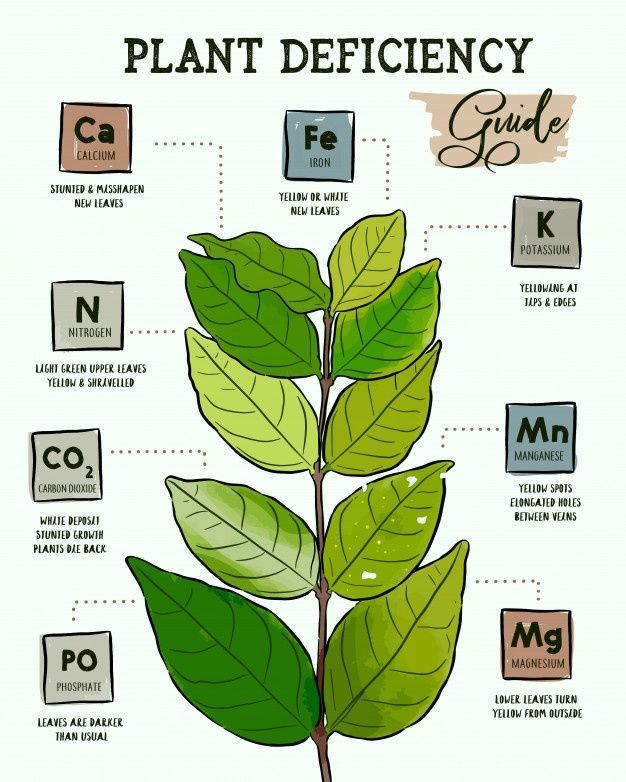
Micronutrients : Essential Elements for Plants
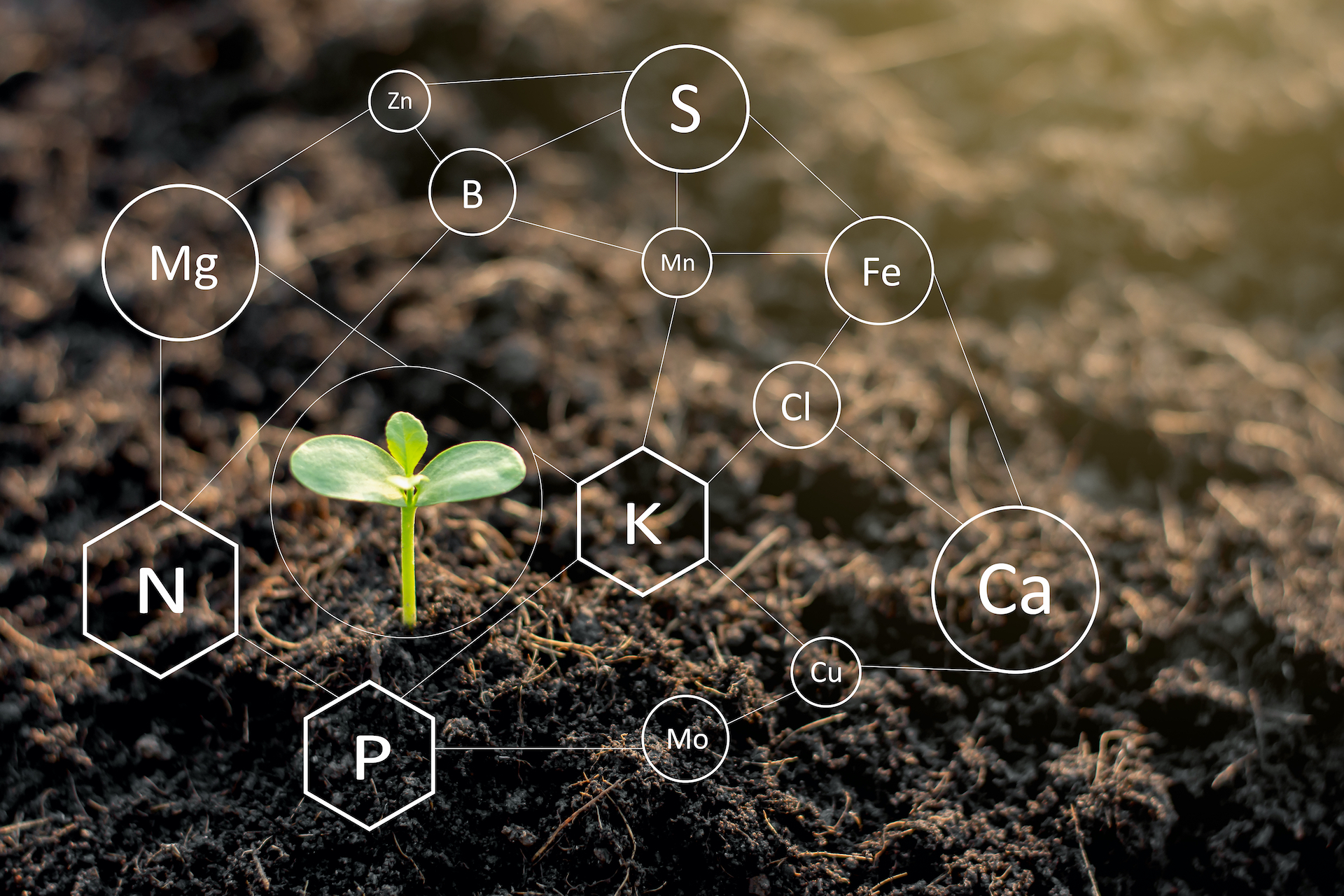
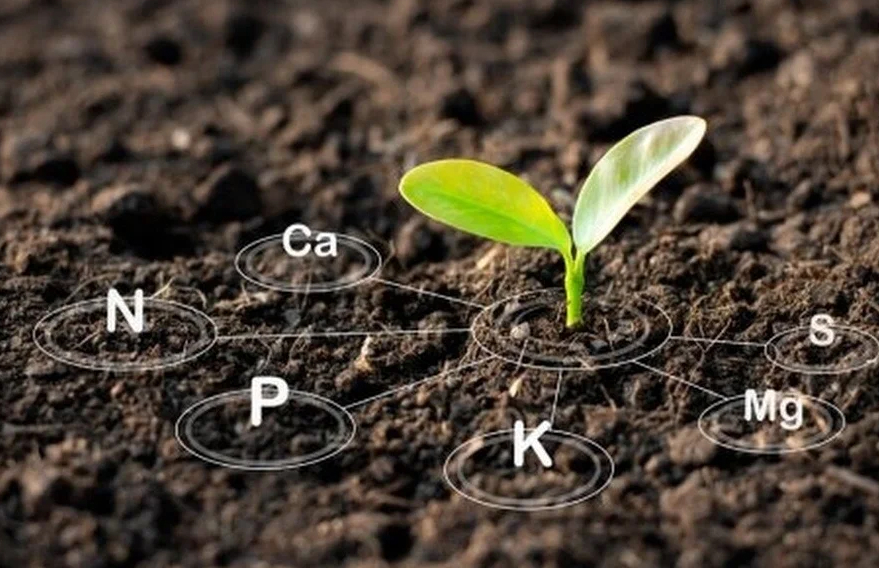
Micronutrients are crucial trace elements that, despite being required in small amounts, play a significant role in plant health and productivity.
These elements include Zinc (Zn), Copper (Cu), Manganese (Mn), Iron (Fe), Boron (B), and Molybdenum (Mo).
They are vital for the proper development of horticultural crops, cereals, pulses, oilseeds, spices, and plantations.
Even though the demand for micronutrients might be low compared to macronutrients, their absence can severely impact plant functions, leading to deformations, reduced yields, and stunted growth.
Hence, maintaining adequate levels of micronutrients is essential for balanced crop nutrition and robust plant development.